Welcome to Agentic AI 101
A beginner-friendly guide to a fast-moving field. No technical background required.
We’re breaking down the basics of agentic AI: what it is, what sets agents apart from the AI you’re used to, and how organizations are already putting it to work. Think of this as your first course in a rapidly evolving field that will evolve as the technology advances.
We’re breaking down the basics of agentic AI: what it is, what sets agents apart from the AI you’re used to, and how organizations are already putting it to work. Think of this as your first course in a rapidly evolving field that will evolve as the technology advances.
Agentic AI explained
Agentic AI is a new class of AI that doesn’t just suggest or assist—it acts. AI agents are autonomous or semi-autonomous software entities that can detect, make decisions, and take action to accomplish goals in digital environments. Agentic AI understands your goals, accesses the tools and data you give it permission to use, and takes initiative to help you move faster, work smarter, and amplify your impact.
In plain terms: Generative AI responds. Agentic AI gets things done—no prompting required.
Agentic AI is the foundation of AI-native work, where intelligence is built into the flow of tasks, understands organizational context, and helps people maximize their work.
In plain terms: Generative AI responds. Agentic AI gets things done—no prompting required.
Agentic AI is the foundation of AI-native work, where intelligence is built into the flow of tasks, understands organizational context, and helps people maximize their work.
AI agent building blocks
Agents on a modern platform share three core attributes: They combine knowledge, skills, and assignments to achieve goals—sometimes with you, sometimes for you.
Knowledge: What AI agents know
AI agents must have secure access to the data and documents needed to complete their tasks—whether from your company’s internal systems, enterprise tools, or third-party sources.
AI agents must have secure access to the data and documents needed to complete their tasks—whether from your company’s internal systems, enterprise tools, or third-party sources.
Skills: What AI agents can do
AI agents don’t just generate content—they perform actions: rewriting text, triggering workflows, annotating docs, and more. These skills are what make agents powerful partners, not just clever copilots.
AI agents don’t just generate content—they perform actions: rewriting text, triggering workflows, annotating docs, and more. These skills are what make agents powerful partners, not just clever copilots.
Assignments: What agents are tasked with
AI agents are embedded into workflows, not siloed in chat. They know when to show up, how to engage with you, and what interface elements to use.
AI agents are embedded into workflows, not siloed in chat. They know when to show up, how to engage with you, and what interface elements to use.
Meet Superhuman Go
Go orchestrates your team of AI agents and makes them available in every tool and tab where you work. Go comes with a powerful set of default agents that you can start experimenting with today, and lets developers build custom ones tailored to your team’s needs.
Find your favorite AI agent
Find your favorite AI agent

By Grammarly
Proofreader
Keep your writing clear and confident.

By Superhuman
Google Calendar
Access your calendar while staying in flow.

By Superhuman
Google Drive
Retrieve info from your files anywhere

By Common Room
Common Room
Helping you reach the right person, at the right time, with the right message, no matter wherever you work

By Superhuman
Outlook Mail
Search, send, and manage your Outlook emails, right when you need them.

By Superhuman
Asana
Manage and track your work with Asana, right where you need it.
AI agent differentiators
There are four key traits that make agents fundamentally different from the AI you’re used to.
AI agents are proactive
AI agents don’t wait for prompts—they anticipate needs. They notice when you’re drafting an email, preparing for a meeting, or managing a backlog, and they appear in the flow of your work to help.
Whether it’s suggesting a rewrite, surfacing key insights, or kicking off a workflow, they take initiative to keep work moving.
Whether it’s suggesting a rewrite, surfacing key insights, or kicking off a workflow, they take initiative to keep work moving.
AI agents are context aware
AI agents understand your task, your tools, your team, and your goals. They don’t offer generic help. They tailor their actions based on what you’re working on and how you work, drawing on past behavior and current context.
The result: smarter support, fewer distractions.
The result: smarter support, fewer distractions.
AI agents are collaborative
AI agents aren’t here to replace you—they’re here to work with you. They take on the repetitive, time-consuming parts of your job while keeping you firmly in control.
You review, approve, and build on their contributions—like working with a teammate who already knows your style and intent.
You review, approve, and build on their contributions—like working with a teammate who already knows your style and intent.
AI agents are permission aware
This is what makes the more sophisticated AI agents enterprise-ready. They operate within the access permissions determined by their users. For instance, you can allow agents to access knowledge and data appropriate to the employee's role, such as a sales target, but not sensitive information.
That makes them not just powerful, but trustworthy.
That makes them not just powerful, but trustworthy.
| Generative AI | AI assistants | Agentic AI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary function | Generate content | Respond to tasks or prompts | Act toward goals with contextual awareness |
| Interaction style | Prompt-based | Conversational, assistive | Proactive, autonomous, and continuously evolving |
| Autonomy | Low | Medium, rule-based | High, outcome-oriented |
| Environment | Stand-alone, prompt-based tools | Pre-integrated tools or platforms | Integrated across systems and workflows |
| Memory | Minimal, session-based | Limited, often short-term | Persistent and adaptive memory that informs behavior |
| Planning ability | None | Reactive logic | Multistep reasoning and dynamic decision-making |
| Output | One-time results, like text or images | Task-based support | Goal-driven outcomes |
Key features of enterprise AI agents
AI agents show up where you work, understand what matters, and drive outcomes across systems.
Ubiquity: AI agents work where you do, so you can stay in flow instead of constantly context switching.
Your agent should be embedded across your workflow—email, docs, Slack, Zendesk—not exclusively trapped in a tab.
Your agent should be embedded across your workflow—email, docs, Slack, Zendesk—not exclusively trapped in a tab.
Contextual intelligence: AI agents understand what matters, so you save time while getting smarter, more relevant outputs.
Real help requires real understanding. Agents should understand your goals, brand, audience, voice, and tone—without needing explicit instructions every time.
Real help requires real understanding. Agents should understand your goals, brand, audience, voice, and tone—without needing explicit instructions every time.
Orchestration: AI agents coordinate across systems, which improves their value and their reach.
Real work spans tools and systems. Agents should operate across apps, triggering actions and passing context fluidly—like a teammate, not a tool.
Real work spans tools and systems. Agents should operate across apps, triggering actions and passing context fluidly—like a teammate, not a tool.
The agentic AI gradient
Not all AI agents are created equal. This gradient shows how agents evolve from simple support tools to complex, autonomous systems.

Why a gradient?
Not every task needs a system of AI agents—and that’s the point. Some problems call for simple, prompt-based tools. Others need coordination across teams, tools, and data. The agentic gradient helps you match the right level of agent to the complexity of your task—from lightweight copilots to fully autonomous systems. It’s about using the right AI for the job.
Think of it like driving: Copilots are like Waze’s GPS suggestions, while multi-agent systems are more like Waymo’s autonomous vehicles. The higher you go on the gradient, the more trust and coordination are required.
Listen to Tim Sanders, VP of Research Insights at G2, break down the agent gradient.
Think of it like driving: Copilots are like Waze’s GPS suggestions, while multi-agent systems are more like Waymo’s autonomous vehicles. The higher you go on the gradient, the more trust and coordination are required.
Listen to Tim Sanders, VP of Research Insights at G2, break down the agent gradient.
Where AI agents are already at work
Agentic AI isn’t theoretical—it’s already powering real work. Here’s how enterprise teams are using agents across the gradient to save time, reduce friction, and accelerate work.

Marketing scenario
Priya, a demand generation manager, is writing an email for a product launch and needs a quick starting point based on existing messaging.
Type of AI agent: Copilot/chatbot
Type of AI agent: Copilot/chatbot
What the AI agent does
- Suggests subject lines and email copy based on a brief prompt
- References the product messaging doc in Coda if linked by the user
- Offers variants tailored to different personas or tones
Why this matters
Priya avoids blank-page syndrome and gets inspired faster—but still retains full control over final edits, audience targeting, and delivery.
Priya avoids blank-page syndrome and gets inspired faster—but still retains full control over final edits, audience targeting, and delivery.

HR scenario
Marco, an HR business partner, is building a Q3 head count plan that aligns with budget and attrition trends.
Type of AI agent: Intelligent AI assistant
Type of AI agent: Intelligent AI assistant
What the AI agent does
- Gathers hiring data from Greenhouse and attrition data from Workday
- Pulls past budget allocations from Excel
- Drafts a summary deck in PowerPoint, complete with narrative and visuals
Why this matters
Marco saves hours of manual compilation and builds a compelling, data-backed plan—making cross-functional alignment easier.

CX scenario
Kevin, a customer success manager, is preparing for a quarterly business review (QBR) and needs a complete, insight-rich view of the account.
Type of AI agent: Task AI agent
Type of AI agent: Task AI agent
What the AI agent does
- Pulls support history from Zendesk and usage metrics from Looker
- Analyzes recent email threads to detect sentiment shifts
- Prepares a draft QBR deck with talking points and recommendations in Google Slides
Why this matters
Kevin spends more time preparing for meaningful conversations, not data gathering—leading to reduced churn and higher customer trust.

Sales scenario
Jess, an account executive, is preparing for a renewal call and needs to personalize her pitch, backed by data and aligned messaging—without hopping across tools.
Type of AI agent: Process AI agents
Type of AI agent: Process AI agents
What the AI agent does
- A briefing agent pulls customer relationship manager (CRM) notes, deal history, and objection-handling insights
- A communications agent scans Gmail and Slack for relevant customer conversations
- A competitive intelligence agent surfaces similar closed-won deals from Gong
- The agent then generates a consolidated prep doc in Google Docs and populates the meeting agenda in her calendar invite
Why this matters
Jess shows up prepared and focused, not buried in tabs or piecing things together. She delivers a strategic, personalized pitch that drives renewals forward.

Product scenario
Nicole, a product manager, is leading the development of a major new feature and needs to coordinate research, data, and planning across multiple teams.
Type of AI agent: System of AI agents
Type of AI agent: System of AI agents
What the AI agent does
- A research agent pulls customer requests from Zendesk
- A revenue analysis agent queries Salesforce to calculate annual recurring revenue
- A documentation agent drafts the product requirements document in Notion following formatting presets
- A stakeholder coordination agent schedules reviews, requests feedback from engineering and design, and updates the Jira roadmap
Why this matters
Nicole focuses on strategy and decision-making, not chasing inputs or formatting slides. Work moves forward in parallel, and decisions are made with data, clarity, and speed.

Marketing scenario
Priya, a demand generation manager, is writing an email for a product launch and needs a quick starting point based on existing messaging.
Type of AI agent: Copilot/chatbot
Type of AI agent: Copilot/chatbot
What the AI agent does
- Suggests subject lines and email copy based on a brief prompt
- References the product messaging doc in Coda if linked by the user
- Offers variants tailored to different personas or tones
Why this matters
Priya avoids blank-page syndrome and gets inspired faster—but still retains full control over final edits, audience targeting, and delivery.
Priya avoids blank-page syndrome and gets inspired faster—but still retains full control over final edits, audience targeting, and delivery.

HR scenario
Marco, an HR business partner, is building a Q3 head count plan that aligns with budget and attrition trends.
Type of AI agent: Intelligent AI assistant
Type of AI agent: Intelligent AI assistant
What the AI agent does
- Gathers hiring data from Greenhouse and attrition data from Workday
- Pulls past budget allocations from Excel
- Drafts a summary deck in PowerPoint, complete with narrative and visuals
Why this matters
Marco saves hours of manual compilation and builds a compelling, data-backed plan—making cross-functional alignment easier.

CX scenario
Kevin, a customer success manager, is preparing for a quarterly business review (QBR) and needs a complete, insight-rich view of the account.
Type of AI agent: Task AI agent
Type of AI agent: Task AI agent
What the AI agent does
- Pulls support history from Zendesk and usage metrics from Looker
- Analyzes recent email threads to detect sentiment shifts
- Prepares a draft QBR deck with talking points and recommendations in Google Slides
Why this matters
Kevin spends more time preparing for meaningful conversations, not data gathering—leading to reduced churn and higher customer trust.

Sales scenario
Jess, an account executive, is preparing for a renewal call and needs to personalize her pitch, backed by data and aligned messaging—without hopping across tools.
Type of AI agent: Process AI agents
Type of AI agent: Process AI agents
What the AI agent does
- A briefing agent pulls customer relationship manager (CRM) notes, deal history, and objection-handling insights
- A communications agent scans Gmail and Slack for relevant customer conversations
- A competitive intelligence agent surfaces similar closed-won deals from Gong
- The agent then generates a consolidated prep doc in Google Docs and populates the meeting agenda in her calendar invite
Why this matters
Jess shows up prepared and focused, not buried in tabs or piecing things together. She delivers a strategic, personalized pitch that drives renewals forward.

Product scenario
Nicole, a product manager, is leading the development of a major new feature and needs to coordinate research, data, and planning across multiple teams.
Type of AI agent: System of AI agents
Type of AI agent: System of AI agents
What the AI agent does
- A research agent pulls customer requests from Zendesk
- A revenue analysis agent queries Salesforce to calculate annual recurring revenue
- A documentation agent drafts the product requirements document in Notion following formatting presets
- A stakeholder coordination agent schedules reviews, requests feedback from engineering and design, and updates the Jira roadmap
Why this matters
Nicole focuses on strategy and decision-making, not chasing inputs or formatting slides. Work moves forward in parallel, and decisions are made with data, clarity, and speed.
How we got here
Agentic AI may feel new, but it didn’t appear overnight. From chessboards and chatbots to copilots and autonomous agents, this timeline shows how decades of breakthroughs laid the groundwork for today’s intelligent systems.
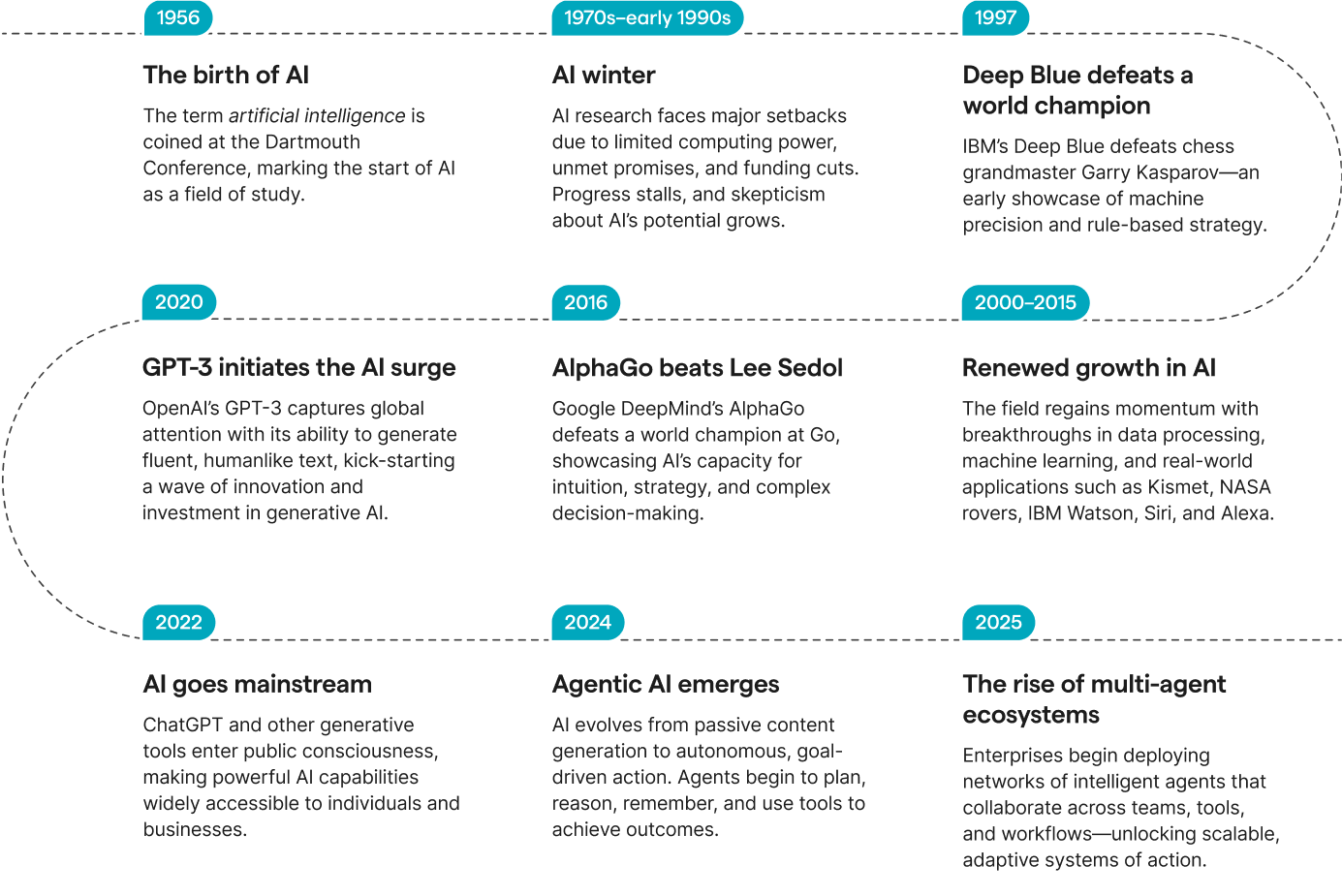
Key terms you need to know
You don’t need a technical background to understand agentic AI. These quick definitions will help you get familiar with the foundational terms that power the field.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
A broad field focused on building systems that simulate the way human minds learn and work using algorithms or logical reasoning. AI can learn and adapt with minimal
human input.
Learn more
Learn more
AI-native
AI-native refers to work, tools, and systems designed from the ground up with AI as a core collaborator, not a bolt-on feature. In AI-native environments, intelligence is built directly into workflows, enabling humans and AI to operate seamlessly together.
Learn more
Learn more
Machine learning (ML)
A subset of AI where systems learn from data, not rules. By recognizing patterns in data, ML allows computers to make predictions and decisions, improving as it processes more information.
Learn more
Learn more
Deep learning
A subset of machine learning that uses layered neural networks to spot complex patterns in large datasets—powering tasks like image recognition, language processing, and predictive analytics.
Learn more
Learn more
Large language models (LLMs)
AI models trained on massive text datasets to understand and generate human-like language. They predict the next word in a sentence, which enables them to write, summarize, answer, and even reason.
Learn more
Learn more
Generative AI
A type of AI that creates new content, such as text, images, or audio, by analyzing vast amounts of data. When given specific prompts, generative AI models can compose an email, write an article, generate ideas, and more.
Learn more
Learn more
Explore more agentic AI resources
You’ve covered the fundamentals. Now take the next step. Explore emerging trends, expert perspectives, and deeper insights into where agentic AI is headed next.

2026 AI Shortlist: 3 Trends Defining the Next Era of AI-Native Productivity

2026 Trends: Solving the AI Productivity Paradox

Making Sense of Summer 2025 Agentic AI Trends

3 Agentic AI Trends Shaping
H2 Plans

How AI Agent Collaboration Will Unlock Enterprise Impact

Why Intuitive Interfaces Will Drive Agentic AI ROI
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between agentic AI and generative AI?
Generative AI tools are reactive—they wait for you to prompt them and respond with content like texts, images, and code. Agentic AI is different. It doesn’t just generate—it acts. Agents take initiative based on your goals, understand your context, and work within your systems to move work forward within the guardrails you set. Instead of being siloed in a chat interface, they show up where you work and collaborate with you to get things done. In plain terms: Generative AI responds. Agentic AI gets things done—no prompting required.
What is an example of agentic AI?
Imagine a customer success manager (CSM) preparing for an important customer meeting. Instead of the CSM having to jump between tools, an AI agent gathers recent support tickets, product usage data, and sentiment from past emails. It then drafts a personalized quarterly business review deck, complete with insights and recommendations, ready for the CSM’s review. That’s agentic AI in action: pulling context, making decisions, and driving outcomes, all without you needing to prompt it.
How do AI agents work?
AI agents combine knowledge (what they know), skills (what they can do), and assignments (what they’re told to do). They access systems and record, make decisions, and take action—all within the permissions you set. This enables them to execute tasks or coordinate workflows with minimal prompting needed.
How can I start using agentic AI in my organization?
Begin by identifying repetitive or high-impact tasks that could benefit from automation. Then explore platforms that support agentic capabilities—especially those that integrate with your existing tools and prioritize security, flexibility, and enterprise control.
What are the benefits of agentic AI?
Agentic AI offers notable benefits to businesses, including improved operational excellence, reduced costs, and a unique competitive advantage.
Cost savings: By automating complex, repeatable tasks without constant input, agentic AI cuts costs while maintaining quality and scalability. Teams can focus on strategic work instead of routine execution.
Operational excellence: AI agents work 24/7, adapt to changing conditions, and improve over time. This means that agentic AI helps businesses accelerate decision-making and remove bottlenecks, leading to quicker and more reliable business operations.
Competitive advantage: Businesses that deploy agentic AI can move faster, scale more efficiently, and deliver smarter experiences, without needing to grow head count. The result: Agentic AI creates a durable edge in a fast-changing market.
Cost savings: By automating complex, repeatable tasks without constant input, agentic AI cuts costs while maintaining quality and scalability. Teams can focus on strategic work instead of routine execution.
Operational excellence: AI agents work 24/7, adapt to changing conditions, and improve over time. This means that agentic AI helps businesses accelerate decision-making and remove bottlenecks, leading to quicker and more reliable business operations.
Competitive advantage: Businesses that deploy agentic AI can move faster, scale more efficiently, and deliver smarter experiences, without needing to grow head count. The result: Agentic AI creates a durable edge in a fast-changing market.
What are the challenges of agentic AI?
Despite its potential, agentic AI comes with several challenges, including ethical concerns and security risks.
Ethical concerns: AI agents act independently, which raises questions about transparency, fairness, and accountability, especially in high-stakes scenarios.
Security risks: Agentic AI’s ability to act autonomously introduces new security vulnerabilities. If compromised, an AI agent can act without oversight, making cybersecurity and controls critical. This high degree of risk makes cybersecurity a critical part of agentic AI development and deployment.
Workforce impact: Agentic AI doesn’t replace human expertise—it frees it up. By offloading repetitive work, AI agents give teams more time for strategy, creativity, and connection. That shift requires thoughtful change management, new roles, and upskilling—but when done right, it unlocks greater potential across your workforce.
Ethical concerns: AI agents act independently, which raises questions about transparency, fairness, and accountability, especially in high-stakes scenarios.
Security risks: Agentic AI’s ability to act autonomously introduces new security vulnerabilities. If compromised, an AI agent can act without oversight, making cybersecurity and controls critical. This high degree of risk makes cybersecurity a critical part of agentic AI development and deployment.
Workforce impact: Agentic AI doesn’t replace human expertise—it frees it up. By offloading repetitive work, AI agents give teams more time for strategy, creativity, and connection. That shift requires thoughtful change management, new roles, and upskilling—but when done right, it unlocks greater potential across your workforce.
Is agentic AI safe to use with sensitive data?
Yes—when it’s built responsibly. Enterprise-ready agentic AI respects user permissions and privacy boundaries. It accesses only the data and tools it’s authorized to use, and many platforms embed guardrails to ensure transparency, control, and compliance.
Do I need technical expertise to use agentic AI?
Not at all. Modern agentic AI platforms are built with usability in mind. Many agents are already embedded directly in tools you use today and don’t require coding or a complex setup. If you can describe your goal, agentic AI can help you achieve it.
Is agentic AI the next big thing?
Yes—and it’s already here. Agentic AI marks a fundamental shift from AI that responds to AI that acts. As organizations move beyond one-off prompts to systems that drive outcomes, agentic AI is becoming the foundation for smarter, faster, more scalable work. It’s not just the next big thing—it’s the next chapter of enterprise intelligence.